Antibody application is a promising therapy in hematological malignancies including acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Unlike for B-cell precursor (BCP-ALL), immunotherapeutic interventions in T-cell ALL (T-ALL) are practically non-existent. Most T-ALL patient samples show substantial surface expression of CD38. Moreover, mice bearing T-ALL patient-derived xenograft (PDX) samples treated with daratumumab (Dara) monotherapy displayed prolonged survival and MRD-negativity in 50% of cases as opposed to animals treated with chemotherapy (Vogiatzi et al., Blood, 2019). Besides CD38, elevated surface expression of CD47 has been described in T-ALL (Chao et al., 2011). CD47 acts as a "don't-eat-me" signal protecting cancer cells from macrophage-dependent phagocytosis. In this study, we explored the efficacy of Dara and a CD47 blocking antibody (Fc-modified version of Hu5F9-G4, termed Hu5F9-IgG2σ) alone or in combination in T-ALL.
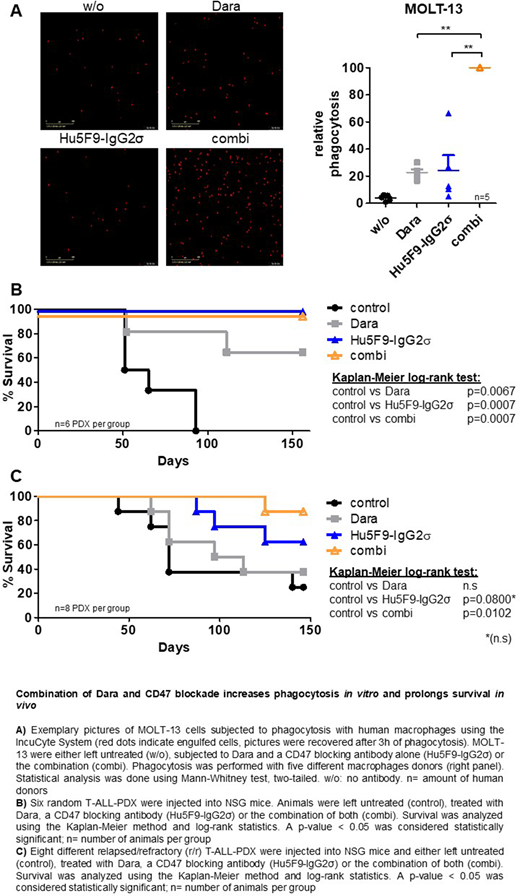
In vitro phagocytosis assays with M-CSF derived M0 (CD64+, CD80-, CD163+) macrophages from healthy donors were evaluated in T-ALL cell lines. Cells labelled with a pH-dependent dye became fluorescent upon engulfment by macrophages and formation of the acidic phagolysosome, which was automatically measured as an absolute cell count. The highest count was set as 100% in each experiment and all other values expressed as percentages relative to that. Treatment of MOLT-13 cells with Dara or Hu5F9-IgG2σ increased median phagocytosis from 5% in control to 23% and 27%, respectively (p=0.008 for both, Figure 1A). However, combined treatment resulted in a maximal increase of median phagocytosis in MOLT-13 cells (p=0.004 compared to Dara and p=0.008 compared to Hu5F9-IgG2σ, Figure 1A). Similar results were obtained in HSB-2 and P-12 cells (p=0.037/0.004 for HSB-2, p=0.011/0.001 for P-12). In addition, phagocytosis was determined in 12 PDX samples from random T-ALL patients. Hu5F9-IgG2σ alone showed a modest increase in median phagocytosis compared to control (19% vs. 6%, p<0.001) and Dara increased phagocytosis to 43% (p<0.001). Combination therapy, however, led to a maximal rise of median phagocytosis in all samples (p<0.001 compared to all others). Phagocytosis was also determined in 16 relapsed/refractory (r/r) T-ALL-PDX samples, in which a maximal median phagocytosis upon combination of Dara and Hu5F9-IgG2σ was also observed (2% in control, 37% in Dara and 14% in Hu5F9-IgG2σ, p<0.001/p=0.02/p=0.02, respectively). The extent of phagocytosis correlated with CD38 and CD47 surface expression on T-ALL cells and, in part, also with expression of signal regulatory protein α (SIRPα) on macrophages, the interacting partner of CD47. A maximal increase in phagocytosis was also observed when applying Hu5F9-IgG2σ in 1/10 of the concentration of Dara, confirming its high efficacy.
The effects of the Dara/ Hu5F9-IgG2σ combination were also examined in vivo in phase II-like preclinical trials containing different patients in one experiment. Six random T-ALL-PDX samples were injected into NOD.Cg-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Wjl/SzJ (NSG) mice and subjected to therapy with Dara and Hu5F9-IgG2σ alone or in combination. In order to mimic minimal residual disease (MRD), antibody therapy was started one day post injection. Mice subjected to Dara displayed prolonged survival in 4/6 (67%) animals compared to control (p=0.007), whereas animals treated with Hu5F9-IgG2σ showed significantly prolonged survival in all cases (p=0.007, Figure 1B). Interestingly, mice not responding to Dara benefitted from Hu5F9-IgG2σ monotherapy and the combination had no further survival advantage in this MRD model. In a second approach, eight r/r T-ALL PDX samples were used, and the same therapy was started upon overt leukemia (1% human blasts in peripheral blood). Compared to control, mice treated with Dara in this overt leukemia and r/r setting showed no survival benefit, while animals subjected to Hu5F9-IgG2σ showed a trend towards a prolonged survival (5/8 cases, 63%, p=0.08). Most importantly, the combination of both agents resulted in a statistically significant survival prolongation in 7/8 cases (88%, p=0.010, Figure 1C).
Altogether, we show that combining Dara with CD47 blockade increases phagocytosis in vitro in three T-ALL cell lines and 28 PDX samples. Our in vivo data suggest that this combination is a highly promising therapeutic strategy, especially in the relapsed/refractory setting.
Cario:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Other: travel support; Novartis: Consultancy, Other: travel support. Kulozik:bluebird bio, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Bourquin:Servier: Other: Travel Support. Schewe:Sobi: Other: was an advisory board member; Bayer: Other: was an advisory board member; Jazz: Other: was an advisory board member; OSE pharmaceuticals: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal